 |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Melanoma Skin Cancer
Melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer. In its advanced state, it can cause serious illness and even death. Fortunately, melanoma rarely strikes without warning. Learn how to identify melanoma, how it spreads and what treatments are available. If it is recognized and treated early, it is nearly 100 percent curable. But if it is not, the cancer can advance and spread to other parts of the body, where it becomes hard to treat and can be fatal. While it is not the most common of the skin cancers, it causes the most deaths. The American Cancer Society estimates that in 2008, there will be 8,420 fatalities in the U.S., 5,400 in men and 3,020 in women. The number of new cases of invasive melanoma is estimated at 62,480; of these, 34,950 will be in men and 27,350 in women. Melanoma is a malignant tumor that originates in melanocytes, the cells which produce the pigment melanin that colors our skin, hair, and eyes. The majority of melanomas are black or brown. However, some melanomas are skin-colored, pink, red, purple, blue or white. Am I at Risk? Everyone is at some risk for melanoma, but increased risk depends on several factors: sun exposure, number of moles on the skin, skin type and family history (genetics). Some people are more at risk than others. Heredity plays a major role. If your mother, father, siblings, or children (first-degree relatives) have had a melanoma, you are part of a melanoma-prone family. Each person with a first-degree relative diagnosed with melanoma has a 50 percent greater chance of developing the disease than members of the general public who do not have a family history of the disease. If the cancer occurred in a grandmother, grandfather, aunt, uncle, niece, or nephew (second-degree relatives), there is still an increase in risk compared to the general population, though it is not as great. Warning Signs Moles, brown spots and growths on the skin are usually harmless — but not always. Anyone who has more than 100 moles is at greater risk for melanoma. The first signs can appear in one or more atypical moles. That's why it's so important to get to know your skin very well and to recognize any changes in the moles on your body. Look for the ABCDEs of melanoma, and if you see one or more, make an appointment with StrikingSkin immediately. An Early Melanoma Recognition Tool A recently developed early detection tool can improve early diagnosis critical to the successful treatment of melanoma. For many years, the early warning signs of melanoma have been identified by the acronym "ABCDE" (A stands for Asymmetry, B stands for Border, C for Color, D for Diameter and E for Evolving or changing was recently added.). While the ABCDE rule helps detect many melanomas, there are a group of melanomas that do not manifest the ABCDE features. Recently, several melanoma specialists developed a new method of sight detection for skin lesions which could be melanoma. Types of Melanoma Melanomas fall into four basic categories. Three of them begin in situ — meaning they occupy only the top layers of the skin — and sometimes become invasive; the fourth is invasive from the start. Invasive melanomas are more serious, as they have penetrated deeper into the skin and may have spread to other areas of the body. |
The facts aboout melanoma:
|
| Content copyright © . Striking Skin by Tanya. All rights reserved. |
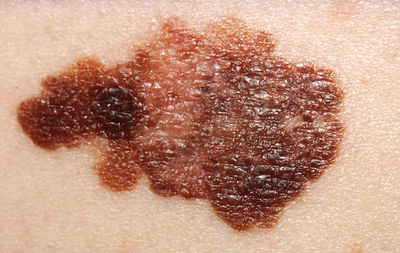 What Is Melanoma?
What Is Melanoma?